It is believed that the most intense pain is a toothache. Although the same can be said for ear pain and headaches. Joint pain is no exception. It can make a person suffer, deprive him of sleep and appetite.
The pain is sharp or dull, stabbing, aching, at night or all day - these are all symptoms of joints.
Prevalence of joint pain
There is no clear pattern between the severity of joint pain and its prevalence. The knee joint can hurt more than the shoulder, elbow and arm at the same time. Sensations in the spine may be painful with extensive osteochondrosis or ankylosing spondylitis. But more often people are bothered by pain in the extremities.
And hands and feet experience significant stress throughout their lives - weight, action, injuries. Pain, joint pain and deformity are inevitable accompanying age-related changes in the musculoskeletal system.
Mechanism of pain
Why do joints hurt is a question that even a doctor finds it difficult to answer categorically.
The mechanism of pain when the musculoskeletal system is damaged is quite complex. Most often, these symptoms are caused by the following processes:
- Inflammation of the joints, or polyarthritis.The inflammation itself triggers the production of substances that can cause pain. In addition, they increase the sensitivity of pain receptors to repeated exposure. That is why the usual load on the inflamed joint leads to a sharp pain reaction.
- Swelling of the joint.Its increase in volume resembles a joint tumor. Edema tissues exert mechanical pressure on joint structures, causing discomfort and aggravating the severity of the process.
- Disruptive changes.This can be called bone and cartilage wear. With age and constant stress, joint function deteriorates. The production of synovial fluid is interrupted and the gliding of the synovial surfaces becomes difficult. Their constant irritation from friction stimulates the growth of subchondral bone. Such marginal bone growths are called osteophytes and can cause real discomfort to a person. They look like protruding bumps on the joints. Osteophytes are often injured, and this causes them to become inflamed, completing the pathological cycle.
- Trauma and post-traumatic complications.Serious injuries: bruises, dislocations, fractures do not go away without leaving traces. Even if the damage heals, pain and stiffness in the joints may remain for the rest of your life. Doctors often deal with complaints of pain in damaged joints. They usually get worse when the weather changes or at night.
- Exchange disorders.Calcifications are deposited in tendons and ligaments due to metabolic disorders. Their violation leads to sharp pain syndrome.
These pathological processes in the joints develop in diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
The number of joint diseases is large. There are rare forms - isolated around the world, and there are those that are found in most people. The prevalence of these diseases explains why everyone has joint pain at least occasionally.
It is important to know the main diseases of the musculoskeletal system, so that you do not ignore the dangerous symptoms, but start treating and treating the disease in time.
Osteoarthritis
Doctors constantly hear from elderly patients that they have pain in the joints of the hands and feet, in the lower back and in the neck. In addition to pain, they complain of joint deformity, difficulty walking and inability to do work.
These symptoms are characteristic of osteoarthritis of the joints. In the case of deformation of the bones and cartilage, it is called deforming osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis deformans in a severe form can make a person completely disabled.
Osteoarthritis affects every joint – big and small. It is only important that they experience enough stress.
If you overload the joints, osteoarthritis will develop several years earlier, especially if there are predisposing factors. These include:
- Fixed load. It can be redundant or monotonous. Static loads play an important role in the development of joint changes.
- Hypothermia or overheating.
- Injuries - bruises and fractures, subluxations and dislocations.
- Excess weight. Fat is one of the most important risk factors for developing osteoarthritis.
- Poor nutrition.
- Lack of movement.
- Infections and subsequent inflammations of the joints are polyarthritis.
Degenerative diseases of the shoulder girdle

The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the body, with the greatest range of motion. It withstands dynamic loads, so degenerative changes in the structures of the shoulder girdle are rare.
They usually develop in old age. Marginal bony growths appear and the articular cartilage atrophies. If the degenerative changes in the shoulder joint are pronounced, then the cause should be sought. This is usually due to a fracture or osteochondromatosis.
Pain in the shoulder joints is painful and constant; stiffness is often associated with degenerative changes in neighboring structures:
- Calcification deposition in the supraspinatus tendon and the resulting painful abduction arch syndrome. With this pathology, pain in the joints occurs when you try to move the shoulder along a certain arc. If you change the angle of inclination, the pain disappears.
- Frozen shoulder syndrome. This condition is characterized by severe stiffness of the shoulder girdle. It occurs as a result of prolonged immobilization of the shoulder - when applying a bandage, providing rest to the hand with thoracic radiculitis.
No pronounced deformation of the elements of the shoulder girdle is observed. Symptoms and complaints related to damage to adjacent structures, rather than osteoarthritis of the shoulder, usually come first.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint
The likelihood of developing degenerative changes in the elbow joint is low. It increases in old age and in people engaged in certain occupations. Monotonous physical activity has a negative impact on joint processes, especially when exposed to vibrations.
Osteoarthritis deformans of the elbow area is often found in tennis players, masons and miners, blacksmiths and foundry workers.
Usually the joint pain is dull, achy and gets worse with exercise. No significant deformation of the joints is observed. Sometimes, under the influence of provoking factors, inflammation of the joints is combined with osteoarthritis, a painful swelling appears in the elbow area, and the pain bothers you even when you are resting.
Osteoarthritis deformans of the hands and finger joints
In recent years, the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hands has become the answer to the question of why finger joints hurt at a young age. This disease is rapidly becoming younger. Already at the age of 30–35 years, with complaints of pain in the finger joints, the signs of the first degree of deforming osteoarthritis can be seen on the X-ray. The reasons for this are varied:
- The number of professions that put pressure on the joints of the hands and fingers is increasing - programmers, typists and just active computer users. And mostly young people are involved in this.
- Working in hypothermic conditions. These are tram and trolley drivers in winter, builders and villagers.
- Absence of normal dynamic loads on finger joints. Few people try to do exercise, especially therapeutic exercises.
- Comorbidities - inflammation of the joints.
The joints of the fingers and hands are deformed over time, and an inflammatory tumor can be detected in the area of the phalanges with the development of polyarthritis. Movements in them become painful and difficult. Joint pain is intermittent at first, but then changes to continuous, dull or aching.
Degenerative diseases of the feet
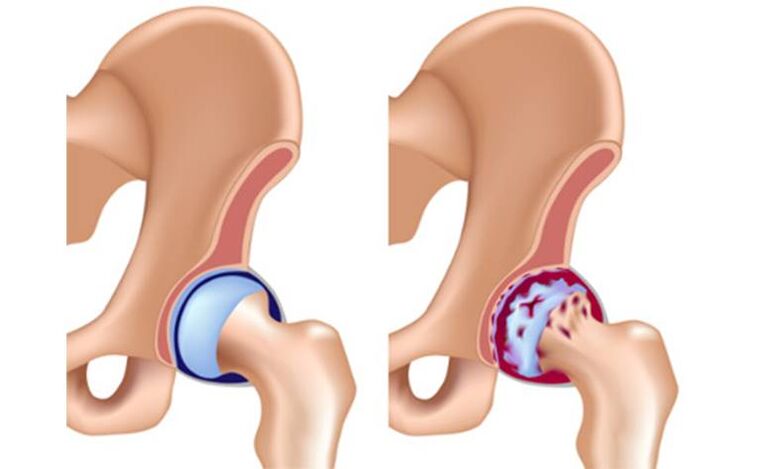
The joints of the legs are more prone to degeneration, since their main load is static. Weight and static loads are the main causes of developing deforming osteoarthritis of the feet. In this area it appears in the following forms:
- Damage to the hip joints - coxarthrosis.
- Damage to the knees with formation of gonoarthrosis.
- Dystrophic diseases of the foot.
Coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis is a common and dangerous disease. Initially, a person pays attention to symptoms such as pain in the joints, tingling, clicking when walking. All these are temporary and do not affect the quality of life much. As the disease progresses, stiffness worsens and difficulty occurs when attempting to abduct or adduct the leg.
Joint pain can be excruciating, debilitating and annoying at any time of the day. In the mornings, my movements are limited, I have to do hip joint exercises to move away.
Genital articulation
Throughout life, the knees face loads that significantly exceed the weight of a person. This inevitably leads to the development of degenerative processes in them. If a person suffers from obesity of at least the first or second degree, the deformation of the knees will occur much faster. In grades three and four, osteoarthritis deforming is more likely to develop at a young age.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joints has its own characteristics. Why does joint pain occur so often in this area? In addition to the proliferation of bony vertebrae and degeneration of cartilage, calcium crystals are deposited in the joint cavity. A kind of deposit of calcifications is formed. This disease is called calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition.
At first they can be found only in the thickness of the cartilage, then on its surface, in the joint cavity, tendons and even muscles.
The deposition of calcium crystals worsens the course of osteoarthritis. The disease manifests itself as pain, which can turn into sharp pain when the calcification bites. The mobility of the legs is significantly limited. In the area of the knees, deformed joint surfaces, bony growths and dense nodules are palpable.
Dystrophic changes in the joints of the legs
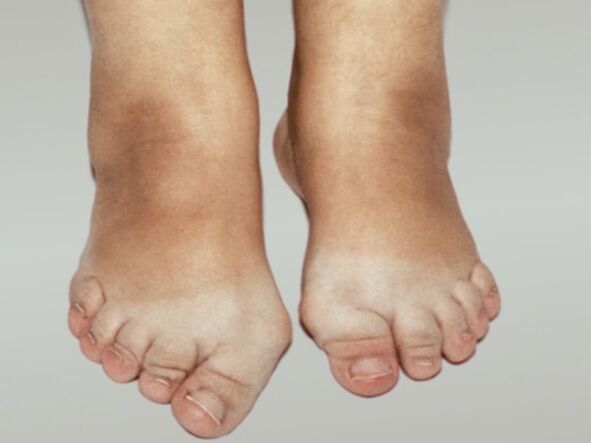
The joints of the feet are less prone to osteoarthritis. An exception is the metacarpophalangeal joint of the first finger. Its deformities appear in almost every person after 55-60 years. In women, it is deformed at a younger age. The reasons for this are the abuse of narrow, uncomfortable shoes with heels.
In addition to the discomfort and anesthetic appearance of a deformed finger, a person experiences severe pain in the joints. As osteophytes grow, protruding bones form around the toe, making it difficult to wear even the widest shoes. Constant injuries to the osteophytes cause inflammation of the finger joints - polyarthritis develops. The situation can be complicated by the addition of an infection.
Inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system
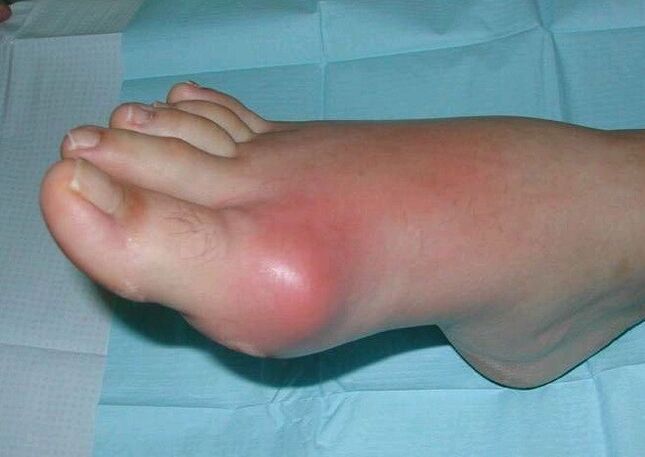
Inflammation of the joints, which affects several groups of joints at the same time, is called polyarthritis. If only one joint is inflamed, this form will be called monoarthritis. Symptoms will depend on the type of inflammation or infection that caused it:
- Joint pain.It is often acute - burning or shooting. If the cause of arthritis is an infection, the inflammation becomes purulent. In this case, the pain will be throbbing and very strong. In chronic and subacute forms, joint pain will resemble the variant with arthropathy.
- Shape change.In an acute process, an inflammatory tumor forms in the joint area, the color of the skin changes and the temperature rises. If a bacterial infection occurs, general symptoms of poisoning appear - high fever, chills, and health deteriorates sharply. The disease is particularly difficult to tolerate in cases of polyarthritis.
- Impaired function.Movement in an inflamed joint is severely restricted due to pain and fluid accumulation in the joint cavity. This swelling, like an inflammatory tumor, mechanically impedes movement.
Causes of arthritis
The causes of arthritis vary. These diseases are usually divided into main groups:
- Infectious.They develop when the joint is directly affected by an infection, such as Lyme disease. The infection can be viral or bacterial, penetrating from outside or from an affected neighboring organ, the bone. Arthritis caused by a bacterial infection is particularly serious.
- Reactive.In this case, the inflammatory process develops as a reaction to a past or present infection. These include damage to the musculoskeletal system after flu, colds and urinary tract infections. An important sign is the connection with infection.
- Autoimmune.Sometimes a person's immune system starts to destroy their own cells. The manifestations of such diseases are varied, but the joint syndrome is usually expressed more clearly. The most common autoimmune pathology is rheumatoid arthritis. It is characterized by severe joint deformation with persistent pain.
Autoimmune polyarthritis is not cured, but must be stopped to keep the disease at an early stage.
Treatment of joint diseases

What to do if diagnosed with joint disease? Should I take drugs, antibiotics or can I limit myself to folk remedies? Only a doctor can answer all the questions correctly and will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies have been prescribed for a long time - both by healers and by modern doctors. They are quite capable of relieving inflammation and eliminating pain by reducing swelling in the affected area.
Among folk remedies, cabbage leaf is considered the undisputed leader. Applying cold or a compress with honey to a painful joint can relieve inflammatory manifestations and relieve the condition. Plantain leaves, chopped mushrooms and vodka liqueur are also used.
The arsenal of folk remedies is varied, but you must remember that they can treat only mild forms of diseases and always under the supervision of a doctor.
Medicines
The drugs used in the treatment of joint diseases target all parts of the pathological process. Main drug groups:
- Analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs.Usually these are drugs of the same group. Since the main symptom of joint diseases is pain, its relief is the doctor's first priority. A good result is achieved when using topical treatments.
- Steroid hormones and cytostatics.It is strictly forbidden to take these drugs without a doctor's prescription. They are used for all serious autoimmune processes and are designed to relieve specific inflammations in the body. Without hormonal drugs, it is impossible to get rid of pain and inflammatory swelling in rheumatoid arthritis. They also prevent joint deformities.
- Antibiotics.They are prescribed if the cause of arthritis is a bacterial infection. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used that penetrate well into bone tissue. Sometimes, if the pathogen is persistent, the doctor can treat the infection using different groups of antibiotics. This is also justified if the disease is caused by mixed infection. It is necessary to remember that antibiotics are powerful drugs with individual side effects and to strictly follow the doctor's instructions during the treatment process.
- Preparations that protect and restore cartilage.It is impossible to treat chronic polyarthritis and degenerative osteoarthritis without chondroprotectors. For this purpose, both individual drugs - chondroitin or glucosamine - and combined are used. There is an extensive evidence base for the use of chondroprotectors based on many clinical trials.
- Intra-articular injections.This is the best way to deliver the medicine directly to the site of the disease. Typically, hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the joint cavity. In recent years, hyaluronic acid has also been used for intra-articular injection.
Physiotherapy

It is not worth treating joint diseases with medicines alone. The integrated use of physical therapy techniques (magnetotherapy, electrophoresis) and physical therapy significantly increases the chances of recovery.
Orthotic devices are also used to limit movement in the affected joints. These include braces and splints. The purpose of these devices is to reduce the load on the affected joint.
Surgical treatment
A radical treatment for advanced osteoarthritis is endoprosthetics. Only this method is capable of replacing a damaged joint with a synthetic one, restoring its full range of motion.
Endoprosthesis replacement is a treatment option in situations where conservative treatment is ineffective.

































